- Home
- Dental Checkup
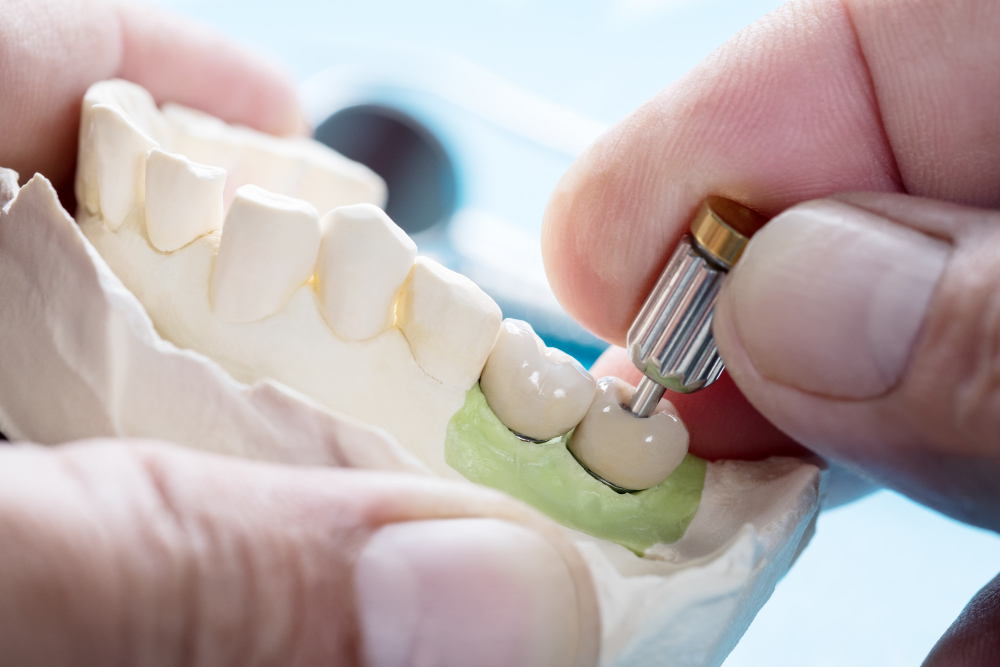
Dental Restorations refer to a range of treatments used to repair or restore damaged, decayed, or missing teeth. These procedures aim to improve the function, structure, and appearance of your teeth, ensuring optimal oral health and a beautiful smile. Restorations can range from simple fillings to more complex treatments such as crowns, bridges, and dentures. Depending on the type and extent of the dental issue, restorations are tailored to meet the individual needs of each patient.
Types of Dental Restorations:
Fillings: Fillings are used to treat cavities caused by tooth decay. The decayed portion of the tooth is removed, and the cavity is filled with materials like composite resin, amalgam, or porcelain to restore the tooth’s function and appearance.
Benefits of Fillings:
Prevent further decay
Restore tooth structure and function
Composite fillings can match the natural color of your teeth, providing a seamless look.
Crowns: A crown is a cap that covers a damaged or weakened tooth to restore its shape, size, and strength. Crowns are often used for teeth that have large fillings, are cracked, or have undergone root canal therapy. Crowns are made from materials like porcelain, metal, or ceramic for durability and natural appearance.
Benefits of Crowns:
Protect a weakened tooth from breaking
Restore the appearance and function of a tooth
Long-lasting solution for damaged teeth
Bridges: A dental bridge is used to replace one or more missing teeth. It consists of a false tooth (pontic) anchored by crowns on the adjacent teeth. Bridges help restore the ability to chew, speak, and maintain the alignment of surrounding teeth.
Benefits of Bridges:
Replace missing teeth
Prevent adjacent teeth from shifting out of place
Restore full chewing function
Dentures: Dentures are removable appliances designed to replace multiple missing teeth. They can be partial (replacing some missing teeth) or full (replacing all teeth on either the upper or lower jaw). Dentures help restore facial appearance and improve chewing ability.
Benefits of Dentures:
Replace multiple missing teeth
Improve speech and chewing ability
Custom-designed for comfort and function
Veneers: Dental veneers are thin, custom-made shells that cover the front surface of the teeth to improve their appearance. They are often used to correct issues like discoloration, chips, or uneven shapes.
Benefits of Veneers:
Enhance the appearance of teeth
Provide a natural, beautiful smile
Durable and long-lasting
Inlays and Onlays: Inlays and onlays are used to restore teeth that have moderate decay or damage. Unlike traditional fillings, inlays and onlays are custom-made in a dental lab and are bonded to the damaged tooth for a precise fit.
Benefits of Inlays/Onlays:
Stronger and more durable than fillings
Preserve more natural tooth structure
Provide a natural appearance
Implants: Dental implants are used to replace missing teeth by placing a titanium post into the jawbone, which serves as a root replacement. Once the implant fuses with the bone, a crown or other restoration is placed on top to complete the tooth replacement.
Benefits of Implants:
Provide a permanent solution for missing teeth
Prevent bone loss in the jaw
Restore function and aesthetics
Why Are Restorations Important?
Functional Restoration: Dental restorations help restore the ability to chew, speak, and perform daily functions comfortably.
Aesthetic Improvement: Restorations enhance the appearance of teeth, improving your smile and overall confidence.
Preventing Further Damage: By repairing damaged or decayed teeth, restorations help prevent more severe dental issues and maintain overall oral health.
Long-Term Health: Proper dental restorations contribute to the longevity of your teeth, preventing additional wear and tear, and supporting overall dental well-being.